
Summertime. Beach weekends. BBQ dinners. Pool parties. Air conditioning problems. Summer is great, but we can all do without the latter. While most of us love to enjoy the fun in the sun, problems occasionally arise with your vehicle air conditioning system that will surely put a dent in your summertime fun.
Vehicle Air Conditioning Operation:
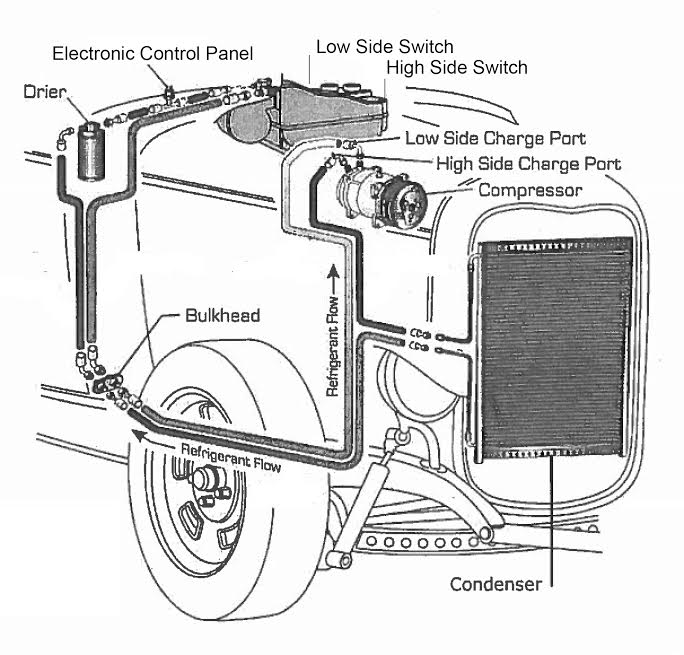
Your vehicle air conditioning system creates cool air by compressing a gas refrigerant known as Freon. Your vehicle air conditioning system converts freon from gas to liquid with a component called a compressor. When activated, the automobile air conditioning compressor pumps vaporized refrigerant under high pressure to the vehicle condenser. The condenser converts the vaporized refrigerant into a liquid, which causes a high amount of heat to be generated during this process. This heat is removed from the condenser by air that flows through the unit. The liquid is then passed along to the next component called a Receiver.
The receiver-drier is a small air conditioning component that acts as a liquid refrigerant reservoir, while simultaneously removing unwanted moisture that may have been inside the refrigerant. Moisture trapped inside an automobile air conditioning system can cause significant problems, including mechanical damage and system blockages caused by ice.
The high pressure liquid refrigerant is then passed from the receiver-drier to the Expansion Valve. The duty of the expansion valve is to eliminate the pressure from the liquid refrigerant. To generate cool temperatures, the high pressure must be removed from the refrigerant. Removing the high pressure allows the refrigerant to expand to become vapor once it reaches the Evaporator, which allows cool temperatures to be generated.
The Evaporator is finned coil that resembles a radiator. Cold, low pressure refrigerant flows through the evaporator. A blower fan then pushes air against the outside of the cold evaporator in order to generate cold air flow into the vehicle. Moisture from the air blown against the cold evaporator causes condensation to build up. This condensation is collected by your vehicle and removed accordingly.
The Compressor then receives the vaporized refrigerant and begins the process again. Since vehicle air conditioning systems do not have a thermostat, the refrigeration cycle continuously runs.
Components of An Automobile’s Air Conditioning System
- Compressor
- Condenser
- Receiver / Drier
- Expansion Valve
- Evaporator
- Blower / Fan
- High Side Switch
- Low Side Switch
- Electronic Control Panel
- Sun Load Temperature Sensor
Automotive Air Conditioning Failure
This is quite a complex system that relies on multiple sub-systems to operate properly. Sometimes a mechanical part goes bad, possibly an electrical control, or perhaps a leak in the system can be the reason for vehicle air conditioning failure. In some cases the vehicle air conditioning system can suffer more than one failure at the same time. Often the diagnosis can be the most technical aspect of the overall job.
Most A/C failures will involve detailed diagnosis, system repair, and or component replacement. We can handle repair or replacement of any vehicle air conditioner component. Ridpath’s is conveniently located on Route 420 in Springfield, Delaware County Pennsylvania. You can count on Ridpath’s Auto Center to walk you through the repair process and return your vehicle’s A/C system to proper working order. We like to think our customers are the “coolest” on the road.
